What is a fortunate swimming bird?
A fortunate swimming bird is a unique concept that combines the beauty of birds with their ability to thrive in aquatic environments. These birds possess qualities that allow them to navigate both land and water, offering us a glimpse into the adaptability of nature. To truly understand what makes a swimming bird fortunate, it is essential to explore their evolutionary traits, environmental benefits, and how they contribute to the ecological balance.
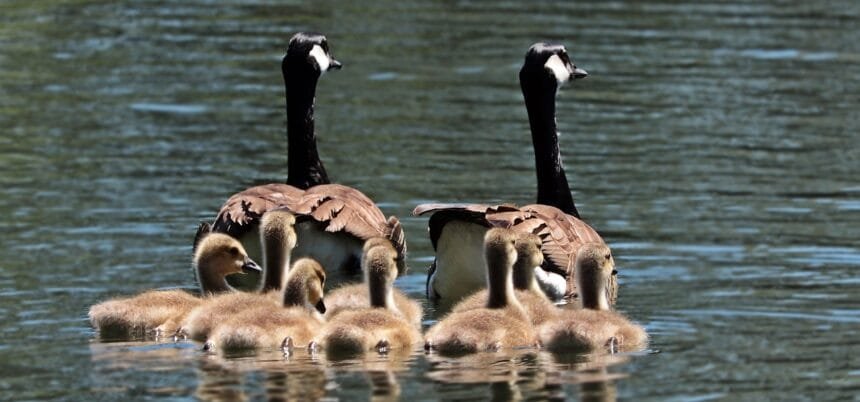
In the natural world, birds are generally known for their flight capabilities. However, there is a special subset of birds that are also skilled swimmers, and these creatures have evolved fascinating ways to survive in both terrestrial and aquatic habitats. Birds like ducks, swans, penguins, and puffins are often referred to as fortunate swimming birds because of their exceptional ability to maneuver through water with ease.
The Evolution of Swimming Birds
When we ask, “What is a fortunate swimming bird?” it is important to recognize that these birds didn’t always exist in their current form. Evolutionary biology plays a critical role in the adaptation of these creatures. Over millions of years, certain species of birds have developed specialized traits that enable them to not only survive in water but thrive in it. These traits include waterproof feathers, webbed feet, and unique body shapes that reduce resistance in water.
For instance, ducks and swans have developed a streamlined body with webbed feet, which helps them paddle efficiently across the water’s surface. Penguins, on the other hand, have a different evolutionary story. These birds have evolved strong wings that function as flippers, allowing them to “fly” through the water, which is essential for hunting fish. What is a fortunate swimming bird? It’s a bird that has mastered the art of both land and water navigation, with evolutionary advantages that make their life in the wild much easier.
The Features that Make Swimming Birds Fortunate
There are several key features that make a bird fortunate in its ability to swim. Some of these features have been fine-tuned over time to ensure their survival in aquatic environments:
- Waterproof Feathers: Birds such as ducks and swans possess waterproof feathers, which help to keep them dry while swimming. This is achieved through the secretion of an oily substance from their preen gland, which coats their feathers and prevents water from soaking through.
- Webbed Feet: Webbed feet are one of the most iconic traits of fortunate swimming birds. These feet function like paddles, making it easier for birds to move through the water. The webbing between their toes helps to push the water backward, propelling them forward with minimal effort.
- Adapted Bodies for Streamlining: Many aquatic birds have streamlined bodies that reduce drag in the water. Their bodies are often elongated and sleek, which enables them to glide effortlessly through water, similar to how fish navigate their aquatic habitats.
- Aquatic Adaptations in Musculature: Birds that spend a significant amount of time in the water, like penguins, have strong muscles, especially in their wings. These powerful muscles allow them to perform aquatic flight, an essential skill for capturing prey.
Why Are Certain Birds Considered Fortunate?
The term “fortunate” is used to describe the advantages that these birds have over others. For birds that are able to swim, their evolutionary traits provide them with the flexibility to survive in multiple ecosystems. A fortunate swimming bird may thrive in an environment where other birds would struggle. For example, ducks can be found in both fresh and saltwater environments and are capable of flying and swimming with equal proficiency. Their ability to migrate across vast distances, from freshwater lakes to coastal regions, gives them access to a wide range of food sources, enhancing their survival chances.
In contrast, birds that are not adapted to swimming might face significant challenges when food is scarce or when they need to escape predators. Swimming birds are less dependent on land-based food sources, and their ability to dive into the water gives them access to a whole new realm of nutrients, which often provides a more diverse diet.
The Benefits of Swimming for These Birds
One of the primary benefits of swimming for fortunate swimming birds is that it opens up a new world of hunting and foraging. Aquatic birds are able to hunt fish, mollusks, and other underwater creatures that are unavailable to their land-dwelling counterparts. For instance, penguins have developed a specialized hunting style, using their flippers to chase and catch fish in the water. Likewise, many ducks and geese feed on aquatic plants and insects that they can easily access by swimming.
Beyond foraging, swimming offers protection from land-based predators. Being able to take to the water for safety can help these birds evade danger when they face threats such as predators on land. A fortunate swimming bird has an adaptive advantage in evading capture, whether by flying to a high place or diving into the water to avoid a predator.
Examples of Fortunate Swimming Birds
To better understand what is a fortunate swimming bird, let’s look at some well-known examples of species that have evolved to thrive in both aquatic and terrestrial habitats.
- Ducks and Swans: These birds are prime examples of fortunate swimming birds. Ducks, in particular, have webbed feet and waterproof feathers, making them excellent swimmers. Swans have long necks and large wings, allowing them to glide through both air and water. These birds are also known for their migratory patterns, traveling between freshwater lakes, rivers, and coastal wetlands.
- Penguins: Perhaps one of the most iconic swimming birds, penguins are adapted for life in the water more than on land. Their wings have evolved into flippers, allowing them to “fly” through the water in pursuit of fish. Penguins are a perfect example of how a bird can adapt to a fully aquatic lifestyle, thriving in cold and temperate waters.
- Puffins: Known for their colorful beaks and distinctive appearance, puffins are another example of fortunate swimming birds. These birds are skilled divers and use their wings to propel themselves underwater, much like penguins. Puffins are able to dive to great depths to catch small fish, making them excellent foragers in the water.
- Kingfishers: Kingfishers are small but powerful swimmers. These birds dive into the water to catch small fish and amphibians, using their sharp beaks to spear their prey. Their ability to dive and swim short distances gives them a significant advantage when hunting.
The Ecological Impact of Fortunate Swimming Birds
The role of fortunate swimming birds in the ecosystem is vast and multifaceted. These birds help maintain balance within their aquatic environments by controlling populations of fish, insects, and other aquatic creatures. Their foraging habits can prevent overpopulation of certain species, helping to maintain a healthy balance in their ecosystem.
Furthermore, fortunate swimming birds contribute to the health of aquatic plants. Ducks, geese, and swans often feed on aquatic plants, which helps prevent the overgrowth of algae and other vegetation. This, in turn, ensures that the water remains oxygenated and healthy for other species.
Another key aspect of the ecological impact of these birds is their role in nutrient cycling. By feeding in the water and then flying or walking on land, swimming birds help to transport nutrients between aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. This nutrient transfer can promote the growth of plants and help create a rich environment for other animals.
The Conservation of Fortunate Swimming Birds
Despite their many adaptations, fortunate swimming birds face a range of threats in the modern world. Climate change, habitat loss, and pollution are all significant challenges that these birds must overcome. Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns can affect the availability of food and nesting sites, while pollution from plastics and chemicals in the water can pose serious threats to their health.
Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure that these birds continue to thrive. Protecting wetlands, coastal habitats, and freshwater lakes is essential for maintaining healthy populations of swimming birds. Organizations around the world are working to protect these environments, reduce pollution, and monitor bird populations to ensure their survival.
Conclusion
In conclusion, what is a fortunate swimming bird? It is a bird that has evolved specialized traits that allow it to navigate both land and water with ease. These birds are lucky in their adaptability, having developed physical and behavioral traits that provide them with significant advantages in the wild. Whether it’s their waterproof feathers, webbed feet, or specialized hunting techniques, swimming birds are a fascinating example of nature’s ability to adapt to diverse environments.
As we continue to learn more about these extraordinary creatures, it is important to remember the vital role they play in maintaining ecological balance and their need for conservation. The fortunate swimming bird is not just a marvel of nature—it is an indicator of the health of our ecosystems and a reminder of the interconnectedness of all living things.
FAQ
1. What is the most well-known fortunate swimming bird?
- The penguin is one of the most well-known swimming birds, adapted for an entirely aquatic lifestyle.
2. Why are swimming birds called fortunate?
- They are considered fortunate due to their unique adaptations that allow them to thrive in both terrestrial and aquatic environments.
3. Can all birds swim?
- No, only a subset of birds, such as ducks, penguins, and puffins, are adapted for swimming.
4. How do swimming birds hunt?
- Swimming birds hunt by diving into the water to catch fish, insects, or other aquatic creatures.
5. Are swimming birds endangered? Some swimming bird species, like certain types of penguins, are endangered due to habitat loss and climate change.